How to Read a Food Label
The Nutrition Facts Label can help you make informed food choices for your healthy diet. Once you have learned how to use the label, you can very quickly decide if the food is a good choice. Follow the color-coded explanations below to understand each section of the label. All labels follow this format, with information about the specific product given in sections 1-4 and the same footnote (5) included on all labels.
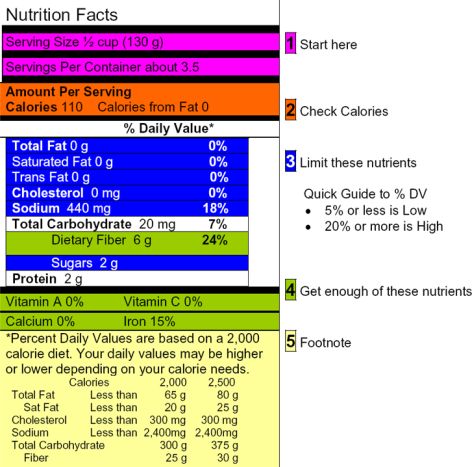
![]() Start here
Start here
The first place to begin is with the serving size and the number of servings in the package. Serving sizes are standardized so you can easily compare similar foods. If you eat the equivalent of 2 servings, you must double the calories and nutrients.
![]() Check Calories
Check Calories
This is the amount of calories per serving, using the correct serving size. When one serving of a food item has over 400 calories per serving, it is high in calories. By looking at calories and nutrients listed on the label you can determine if the food is worth eating.
Calories from Fat: These are calories solely from fat. Focus on getting fat in your diet from monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats. Skip food products that contain trans and saturated fats.
![]() Limit these nutrients
Limit these nutrients
These are nutrients most people eat in adequate amounts or even too much. Eating too much fat, saturated fat, trans fat, cholesterol or sodium may increase your risk of certain chronic diseases, like heart disease, some cancers or high blood pressure.
Sugars refer to both natural and added sugars. Read the ingredient list to find added sugars, which can be listed as sugar, sucrose, glucose, high fructose corn syrup, corn syrup, maple syrup, honey and fructose. If sugar is among the first few ingredients, the food is high in added sugar. Since added sugar contributes empty calories, look for foods and beverages low in added sugars.
![]() Get enough of these nutrients
Get enough of these nutrients
Most people have to work hard to get enough fiber, vitamin A, vitamin C, calcium and iron in their diet. Eating the right amount of these nutrients can help in the prevention of some diseases and conditions. Foods with 5 grams of fiber or more are considered “high fiber” foods. Vitamins and minerals are shown as percentages. The goal is to consume 100% of each of these nutrients daily to prevent nutrition related diseases.
![]() Footnote
Footnote
The statement “*Percent Daily Values are based on a 2,000 calorie diet,” must appear on all food labels. If the package is small, the rest of this section may not appear. The full footnote is always the same, because it shows recommended dietary advice, not information about the food in the package. Daily Values are recommended levels of intakes. They are shown for a 2,000 calorie and a 2,500 calorie diet.
Quick tips for reading a nutrition food label:
- Begin with reading how many servings per package and the calories per serving.
- Avoid foods with trans-fat and saturated fats.
- Scan cholesterol. Less than 20 milligrams per serving is considered low.
- Limit sodium. Less than 140 milligrams per serving is considered low.
- Pick foods with fiber, ideally greater than 5 grams per serving. Remember any amount of fiber is still beneficial.
- For milligrams of calcium replace the % sign with a zero and now you will have milligrams.
It is important to use food labels not only to limit the nutrients you want to cut back on but to focus on those nutrients you want to increase in your diet in greater amounts such as fiber and calcium. Food labels can be of great use when picking up a new item you are not familiar with to explore if it is a healthy choice. Having basic knowledge of nutrition will enable you to put all the information you have acquired to good use when reviewing food labels.
Product has less than one gram of fat per serving:
Fat-free: Product has less than ½ gram of fat per serving.
99% Fat-free: Every 100 grams of food will have 1 gram or less of fat.
Low-fat: Has 3 grams of fat or less per serving.
Reduced-fat: Fat has been reduced by at least 25 percent when compared to a similar food product.
Light product: Has 33% fewer calories or 50% less fat per serving than a comparable product.
Lean: Used for meat and poultry only. Product has less than 10 grams fat, less than 4 grams saturated fat, and less than 95 milligrams cholesterol per serving.
Low-calorie: Product has 40 calories or less per serving.
Saturated fat-free: Product has less than 0.5 grams saturated fat per serving.
Trans fat-free: Product has less than 0.5 grams trans fat per serving.
Low in saturated fat: Product has one gram or less saturated fat per serving.
Cholesterol free: Product has less than 2 milligrams of cholesterol per serving.
Low cholesterol: Product has less than 20 milligrams or less cholesterol and two grams or less of saturated fat per serving.
Sodium-free: Product has less than 5 milligrams of sodium per serving.
Very low sodium: Product has 35 milligrams or less of sodium per serving.
Low-sodium: Product has 140 milligrams or less of sodium per serving.
Good source: Used for fiber, protein, vitamins or minerals. Product has at least 10% of the Daily Value for a particular nutrient.
High In (Excellent Source): Used for fiber, protein, vitamins or minerals. Product has at least 20% of the Daily Value for a particular nutrient.

 Follow
Follow